 |
Three-dimensional Fabry-Perot data visualization is a complex problem
which may be solved as advanced 3D graphics systems become more
commonly available over the next few years. FPTOOL approaches
this issue by providing interdependent visualization of both the
spatial and spectral domains of the data. (See
Shopbell & Bland-Hawthorn
1995
;
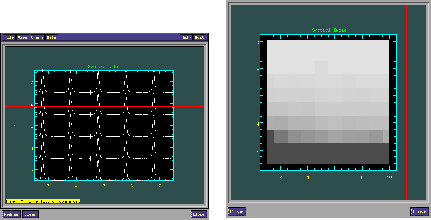
Figure 1.) As shown in Figure 1, the two primary windows provided by
FPTOOL are an image display window and a spectral grid display
window. This approach is simpler to develop and eliminates the steep
learning curves of many 3D visualization tools, since each of the
windows are familiar to the observational data analyst.
The image display window resembles an ximtool window, although the controls have been developed specifically for Fabry-Perot imagery. The primary control is a scroll bar which allows the user to select a frame along the spectral (Z) dimension for display. Multiple frames may be selected and the binned result displayed as well, in order to examine the flux from an entire line profile, for example. The scroll bar can be scanned to demonstrate trends in the line profiles over both spatial and spectral domains. Since it is intended for use in data analysis and not final presentation, the image display window does not provide the degree of detail and customization (e.g., colormap selection) that is found in the ximtool client.
The spectral display window resembles other tools used in slit spectra analysis, such as IRAF's SPLOT. The most significant enhancement in FPTOOL has been the addition of support for two-dimensional grids of spectra. Just as with the image display window, scroll bars are provided for scanning along the spatial (X, Y) axes of the data cube. The window into the spectral domain may thereby be moved throughout the spatial field of view. The grid may be zoomed, stretched, and binned as well.
Finally, the image and spectral display windows are interactively linked: a box (``marker'' in IRAF GUI terms) is maintained in the image display window to indicate the spatial extent of the spectra displayed in the spectral window. This box is not merely illustrative, however, and may be moved and resized to select a desired field of spectra for display.